Affordances of agricultural systems analysis tools: A review and framework to enhance tool design and implementation
Abstract
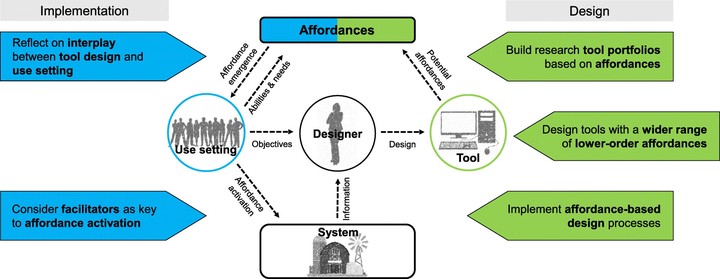
The increasingly complex challenges facing agricultural systems require problem-solving processes and systems analysis (SA) tools that engage multiple actors across disciplines. In this article, we employ the theory of affordances to unravel what tools may furnish users, and how those affordances contribute to a tool’s usefulness in co-design and co-innovation processes. Affordance is defined as a function provided by an object through an interaction with a user. We first present a conceptual framework to assess the affordances of SA tools. This framework is then applied in a literature review of three SA tools used in agricultural systems research (fuzzy cognitive mapping, bio-economic whole-farm models, and role play and serious games). Through this exercise, we extend the SA tool design and implementation dialogue by illuminating (i) links between lower-level affordances, tool design, and heuristic functioning, and (ii) the central role of use setting and facilitation in mobilizing higher-level, productive affordances. Based on our findings, we make five propositions for how SA tool design and implementation in participatory problem-solving settings can be improved.